Tue, Feb 18, 2020
Malware Analysis - Buran Ransomware-as-a-Service
In September 2019, Kroll reported on Buran ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) being offered on the top-tier Russian Forum, Exploit. Buran is one of the numerous ransomware variants operating as a RaaS program; in Buran’s case, affiliate distributors give 25% of their ransom profits to “buransupport” to obtain a decryption key. In November 2019, the actors behind the “buransupport” moniker began to advertise a second ransomware variant, Zeppelin, which has been observed to have data exfiltration capabilities. Kroll assesses that this new feature may have been prompted by the tactics of other ransomware threat actor groups, who are actively publicizing data stolen from victims who have refused to pay ransom demands.
Since Buran’s launch, Kroll analysts have observed multiple updates to the ransomware being advertised on dark web forums. In addition to being spread via RIG exploit kits and malspam campaigns, Kroll incident responders have also observed Buran being spread via misconfigured Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
Buran is advertised as a fully offline crypto-locker written in Delphi code that claims to work on every Windows operating system, starting with Windows XP/Windows Server 2003. (See Figure 1 for a representative dark web listing.) Based on tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs), Buran is considered to be a variant of VegaLocker ransomware.
|
Attack Vector |
Infection vectors vary based on the specific version of Buran; primary methods have involved a RIG exploit kit1 or malspam:
|
|
Kroll-Observed Attack Vector |
Kroll incident response teams have observed the ransomware spreading via RDP access coupled with privilege escalation. In one case, an organization’s RDP was misconfigured to be open to the internet:
In another Kroll investigation, the actor(s) actively cleared event logs and deleted Windows volume snapshots, making it difficult to ascertain the initial infection vector:
|
|
Dark Web Updates |
Kroll has observed that since being advertised in May 2019, Buran has been updated on six separate occasions.
|
|
Startup and IOCs |
|
|
Preemptive Recommendations |
|
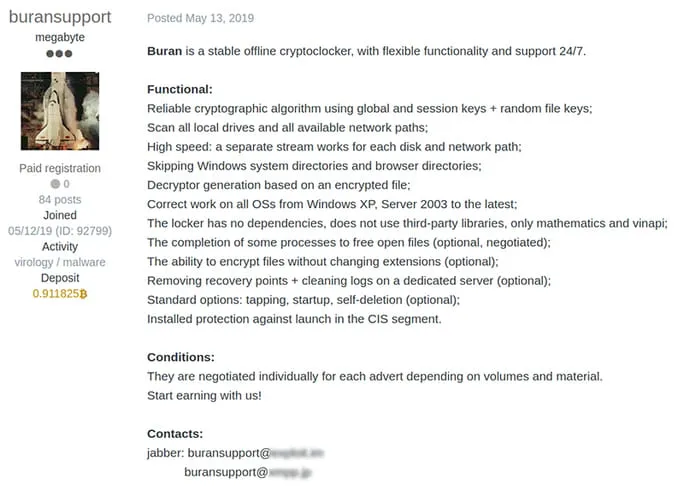
Figure 1 – Buran listing on dark web
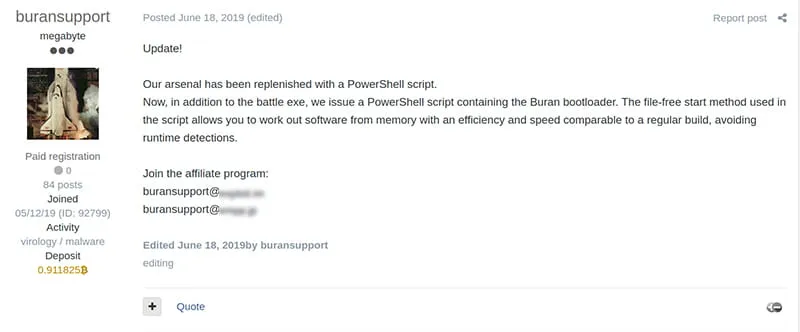
Figure 2 – Dark Web Listing, June 2019 Update to Buran Supporting PowerShell Bootloader
| IOC |
Type |
Description |
|
45.142.213.167 |
IP Address |
Identified in bat.exe file - download attempt |
|
hxxp://45.142.213.167/oxf |
URL |
URLs hosted on this IP address: 45.142.213.167 |
|
hxxp://45.142.213.167/reg |
URL |
URLs hosted on this IP address: 45.142.213.167 |
|
hxxp://192.119.68.225/wordupd1.tmp |
Payload |
|
|
hxxp://108.174.199.10/wordupd3.tmp |
Payload |
|
|
hxxp://54.39.233.175/wupd19823.tmp |
Payload |
|
|
hxxp://54.39.233.131/word1.tmp |
Payload |
|
|
def.exe |
exe |
Disables Windows Defender; hides the control panel; contacts 45.142.213.167; found in C:\temp |
|
bat.exe |
exe toolset |
Actor toolset; found in C:\temp
|
|
Advanced_Port_Scanner_2.5.3869.exe |
|
Port scanner, network reconnaissance tool
|
|
buran_2019-06-28_04-40.exe |
|
Buran ransomware |
|
Everything.exe |
|
Windows system reconnaissance tool |
|
load.exe |
|
Unknown, unrecoverable |
|
lsass_2006.exe |
|
Unrecoverable, likely credential stealing malware based on name |
|
lsass_2206.exe |
|
Unrecoverable, likely credential stealing malware based on name |
|
mimikatz.exe |
|
Unrecoverable, likely credential stealing malware based on name |
|
Processhacker-2.39-setup.exe |
|
ProcessHacker – Windows process auditing tool |
|
Total-Uninstall-Setup-6.23.0.exe |
|
Total Uninstaller application uninstaller tool |
|
TUPortable_6.3.4.100_32bit_64bit_Multilingual.paf.exe |
|
Total Uninstaller application uninstaller tool |
|
unlocker.exe |
|
Windows file unlocking tool |
|
Ilivenutm_trWorldwidepop |
|
|
|
filestake@tutanota[.]com |
|
|
|
polssh1@protonmail[.]com |
|
|
|
polsshprotonmail[.]com |
|
|
|
unique10@protonmail[.]com |
|
|
|
rizonlocker@airmail[.]cc |
|
|
|
realtime5@protonmail[.]com |
|
|
|
wtfsupport@airmail[.]cc |
|
|
|
wtfsupport@cock[.]li |
|
|
|
filestake@mailfence[.]com |
|
|
|
rizonlocker@firemail[.]cc |
|
|
|
61fd307906f8755516f0acd2e59c25dc |
|
|
|
e60e767e33acf49c02568a79d9cbdadd |
|
|
|
5c9fc92ab44374e1fdafd49808b2f638 |
|
|
|
f88de5fc23b74f5066777e120232735f |
|
|
|
55030a1c4072b1b0b3c33ba32003b8b5 |
|
|
|
4266d31978d357c618c5839404850910 |
|
|
Figure 3 - Indicators of Compromise (as of this alert)3
Sources
1 Exploit kit (“EK”) is a set/toolkit of software designed to exploit a security vulnerability in other software.
2 hxxps://fortiguard.com/encyclopedia/endpoint-vuln/57091
3 IOC information was obtained via multiple sources including Kroll incident response data. Contact Kroll for more information on sourcing.
Cyber and Data Resilience
Incident response, digital forensics, breach notification, security strategy, managed security services, discovery solutions, security transformation.
24x7 Incident Response
Kroll is the largest global IR provider with experienced responders who can handle the entire security incident lifecycle.
Data Breach Notification Services
Services include drafting communications, full-service mailing, alternate notifications.


